Hidden Files#
By default some of the folders (directories) and files are hidden on your computer to protect you against making changes that causes problems. You will need to see some of these files and folders to properly set up and use the software described in this book.
Change Settings via a GUI#
Mac OS#
This is very easy to do on a Mac, simply use the following keyboard combination (i.e., holding three buttons simultaneously):
Command + Shift + .
If this doesn’t work, try a Google search for “Finding hidden files on a Mac” and look for an explanation that includes a computer and OS similar to your personal setup.
Windows OS#
Settings for hidden files and folders can be found directly via the Windows File Explorer. First find the “options” or “settings” configuration window (sometimes pressing the ALT button toggles the menubar on and off):
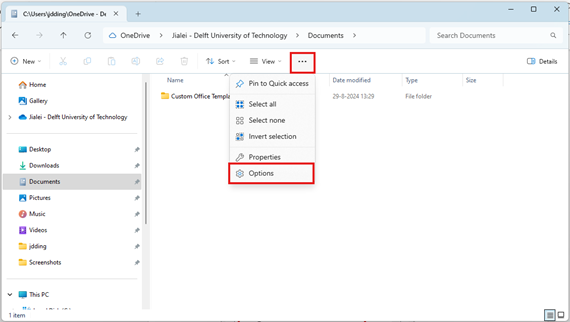
Fig. 11 Find the options window for your directory (Windows).#
Then navigate to the proper location in the “View” tab of the Folder Options window:
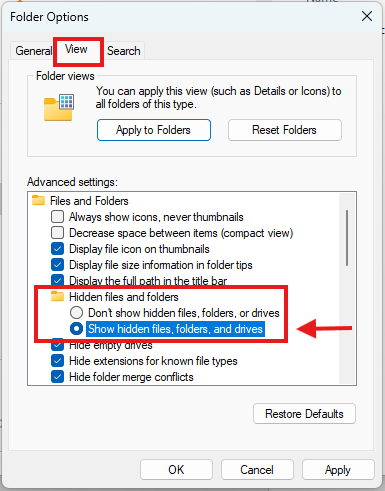
Fig. 12 Show hidden files and folders for your directory (Windows).#
Use the Command Line Interface (CLI)#
If you would like to view hidden files and folders via the command line, this is illustrated with the simple commands here (review the CLI page for an overview of the different systems):
The option a lists all files (including hidden ones) and the l presents the output in a nicely formatted list (one item per row):
ls -la
The command:
dir /a:h
will list hidden files in the current directory, whereas the following will list hidden directories:
dir /a:d
There are two options to try:
Get-ChildItem -Force
dir -Force
In case you run into trouble here, try this Stack Exchange answer.
